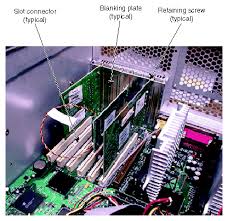
– is the most
complicated part of a PC. It houses the actual computing power of the system,
provides connections to all the peripherals, and holds the disk drives where
you insert removable storage media such as CDs and floppy disks.
Ports - a generic
term for connection points.
Power Input
- is where you
plug in the PC’s electrical power cord.
Mouse port
- this dedicated
port is just for the mouse.
Keyboard
port
– this special
dedicated port is just for the keyboard.
USB ports
– universal
serial bus (USB) ports are general-purpose connectors found on newer PCs. The more unusual the peripheral, the more
likely it will use USB port.
Serial ports
– these 9-pin
connectors is one of the oldest and most universal port found in the back of a PC. Before the introduction of USB in the
mid 1990s, serial ports where heavily used.
Parallel port
– virtually as
old as the serial port, the 25–pin parallel port has been updated a number of
times over the ye3ars. Despite the growing prominence of USB, parallel ports
remain a popular means for connecting printers.
Video
port
– this unique
three-row, 15-pin connector is where the monitor connects to the system unit.
Audio ports
– these are used
to connect speakers, microphones, and other audio devices.
Game port
– also known as
a joystick port, this 15-pin connector can be used both for joysticks and for
MIDI musical devices.
Modem port
– this looks like a telephone jack, and
for a good reason – that’s what’s it
is. Modem enables your computer to communicate with other computers via
telephone line. Notice that there are two connectors. One is an IN jack, and
the other is an OUT jack, which you can use to plug in a telephone.
Network interface/LAN Port
– the network interface is
normally called just that, and not a port. It is sometimes referred to as an Ethernet connector. It connects your PC
to other PC’s in a Local Area Network.